Aquaculture wastewater
Publisher:adminNumber of views:
The daily discharge of wastewater from large-scale aquaculture farms is large and concentrated, and the wastewater contains a large amount of pollutants, mainly heavy metals, residual veterinary drugs, and a large number of pathogens. Therefore, if discharged into the environment or directly used for agriculture without treatment, it will cause serious pollution to the local ecological environment and agricultural fields.
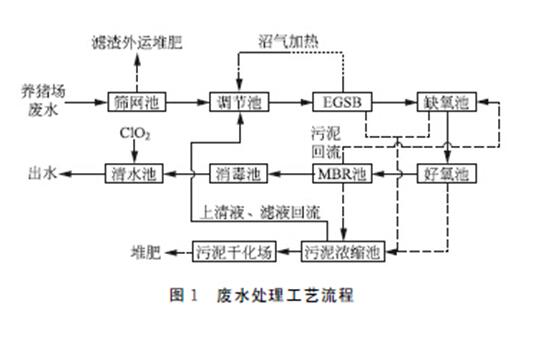
Aquaculture wastewater has typical "three high" characteristics, including high CODcr, high ammonia nitrogen, high SS, and is prone to producing foul odor. At present, a single treatment method cannot meet the requirements of wastewater discharge standards. Livestock and poultry breeding wastewater generally requires a combination of multiple treatment technologies. Our company adopts an anaerobic combined with aerobic treatment method, and the treatment process is shown in the figure:
The aquaculture wastewater enters the regulating tank after removing impurities and large particle waste residue through a screening tank. After pre-treatment, the wastewater enters the EGSB reactor, where the particle sludge bed inside the reactor is in a partially or fully expanded state. The effluent reflux technology is used, and the liquid in the reactor has a high upward flow rate. The effluent reflux can dilute the concentration of sulfates and other toxic and harmful substances, and the wastewater can be in full contact with microorganisms, It can withstand large organic loads, effectively avoiding the generation of dead corners and short flows in the reactor, and has the characteristics of high volumetric load and high treatment efficiency for pig farm wastewater. The protein and other macromolecular organic substances in the wastewater of EGSB are first decomposed into small molecule substances under the action of anaerobic bacteria, and then small molecule substances are degraded into CH4 and other substances through the action of methane bacteria; EGSB effluent enters the anoxic and aerobic tanks in sequence, further degrading organic matter. Then the wastewater enters the MBR tank for advanced treatment. The effluent from the MBR tank enters the disinfection tank, and some of the sludge flows back to the anoxic tank. After being disinfected with chlorine dioxide, it flows by gravity to the clean water tank for discharge. The excess sludge generated by the system is concentrated, dried, and then transported for composting. The filtrate and supernatant from the sludge concentration tank return to the regulating tank.

Aquaculture wastewater has typical "three high" characteristics, including high CODcr, high ammonia nitrogen, high SS, and is prone to producing foul odor. At present, a single treatment method cannot meet the requirements of wastewater discharge standards. Livestock and poultry breeding wastewater generally requires a combination of multiple treatment technologies. Our company adopts an anaerobic combined with aerobic treatment method, and the treatment process is shown in the figure:
The aquaculture wastewater enters the regulating tank after removing impurities and large particle waste residue through a screening tank. After pre-treatment, the wastewater enters the EGSB reactor, where the particle sludge bed inside the reactor is in a partially or fully expanded state. The effluent reflux technology is used, and the liquid in the reactor has a high upward flow rate. The effluent reflux can dilute the concentration of sulfates and other toxic and harmful substances, and the wastewater can be in full contact with microorganisms, It can withstand large organic loads, effectively avoiding the generation of dead corners and short flows in the reactor, and has the characteristics of high volumetric load and high treatment efficiency for pig farm wastewater. The protein and other macromolecular organic substances in the wastewater of EGSB are first decomposed into small molecule substances under the action of anaerobic bacteria, and then small molecule substances are degraded into CH4 and other substances through the action of methane bacteria; EGSB effluent enters the anoxic and aerobic tanks in sequence, further degrading organic matter. Then the wastewater enters the MBR tank for advanced treatment. The effluent from the MBR tank enters the disinfection tank, and some of the sludge flows back to the anoxic tank. After being disinfected with chlorine dioxide, it flows by gravity to the clean water tank for discharge. The excess sludge generated by the system is concentrated, dried, and then transported for composting. The filtrate and supernatant from the sludge concentration tank return to the regulating tank.






